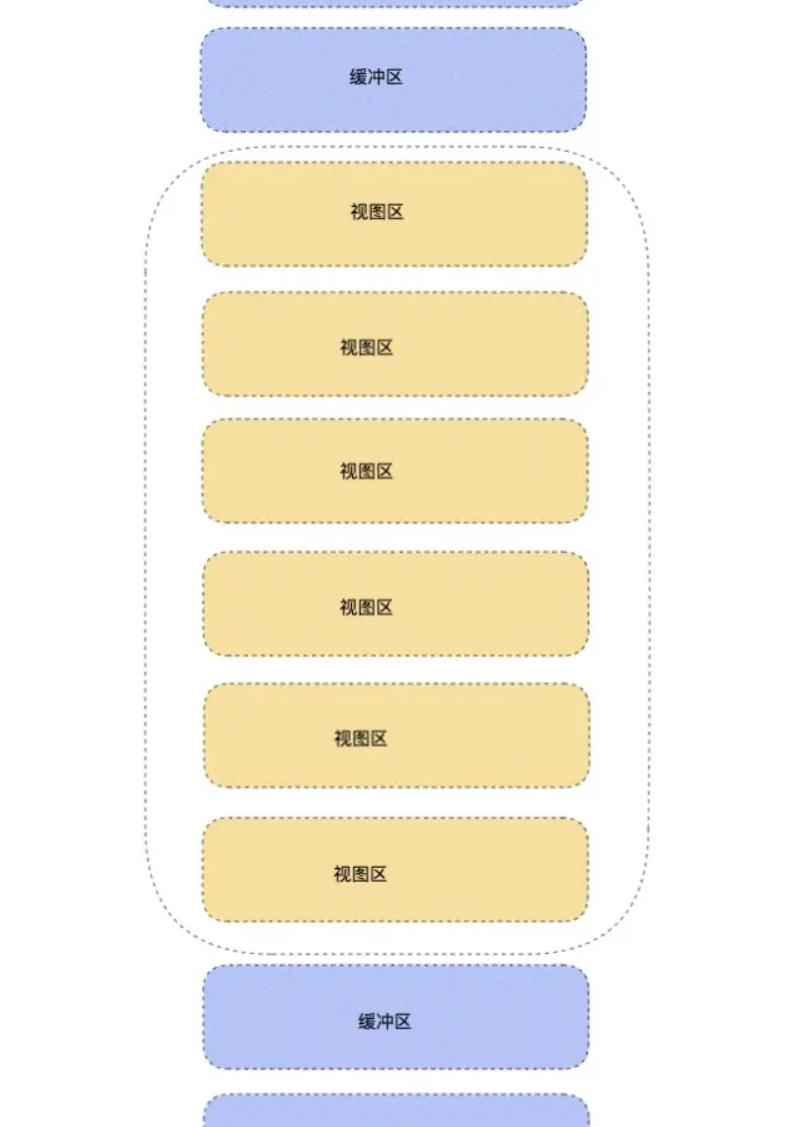
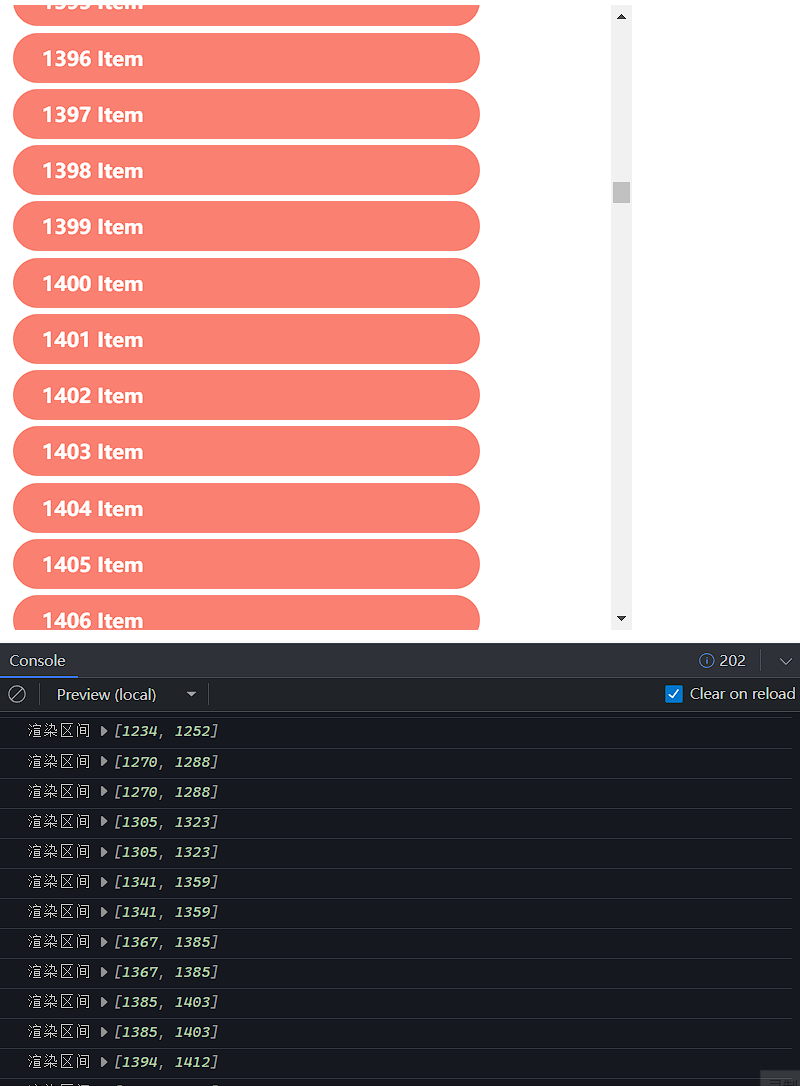
import { useEffect, useMemo, useRef, useState } from "react";
import "./index.css";
function getColor() {
const r = Math.floor(Math.random() * 255);
const g = Math.floor(Math.random() * 255);
const b = Math.floor(Math.random() * 255);
return "rgba(" + r + "," + g + "," + b + ",0.8)";
}
function getPostion(position) {
const { width, height } = position;
return {
left: Math.ceil(Math.random() * width) + "px",
top: Math.ceil(Math.random() * height) + "px",
};
}
function Circle({ position }) {
const style = useMemo(() => {
return {
background: getColor(),
...getPostion(position),
};
}, [position]);
return <div style={style} className="circle"></div>;
}
function Box() {
const [state, setState] = useState({
dataList: [],
renderList: [],
position: { width: 0, height: 0 },
});
const boxRef = useRef(null);
useEffect(() => {
if (!boxRef.current) {
return;
}
const { offsetHeight, offsetWidth } = boxRef.current;
const originList = Array.from({ length: 20000 });
setState({
position: { height: offsetHeight, width: offsetWidth },
dataList: originList,
renderList: originList,
});
}, []);
return (
<div className="box" ref={boxRef}>
{state.renderList.map((item, index) => (
<Circle position={state.position} key={item + index + ""} />
))}
</div>
);
}
export default function Index() {
const [show, setShow] = useState(false);
return (
<div
style={{
width: "100%",
height: "100%",
}}
>
<button onClick={() => setShow(true)}>show</button>
{show && <Box />}
</div>
);
}
|